Caution
This is the documentation for the current development branch of the CometVisu. It is possible that some of the described features are not yet available in the current release.
Also there might be lots of errors in this documentation as some parts of the content have been translated by an online translation service.
The ColorChooser widget
Description
The ColorChooser let you select and display a color, e.g. for lighting effects. It supports a RGB light source with red, green and blue light components as well as a RGBW light source that also has a white channel.
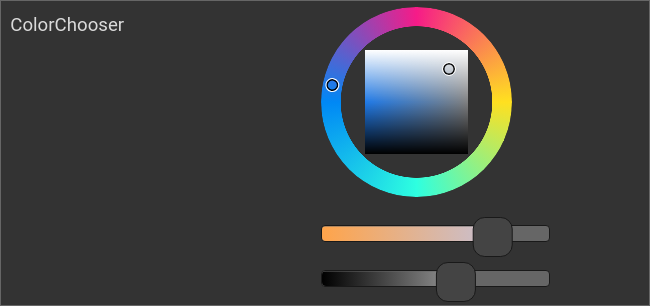
The ColorChooser
<colorchooser controls="LCh-box;T:2500-15000;Y">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="6"/>
<label>ColorChooser</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Simple mode
For most use cases the simple mode will be sufficient. It is optimized for a simple configuration by ignoring a perfect color consistency between lighting and display.
Widget components: slider
The ColorChooser offers different possibilities and combinations for selecting and displaying of a color. There are sliders for a direct control of a color channel, but also some for a indirect modification of a channel by representing a part of a color in the way a human is experiencing it.
|
red channel - direct control of RGB-lighting |
|
green channel - direct control of RGB-lighting |
|
blue channel - direct control of RGB-lighting |
|
red channel - direct control of RGBW-lighting |
|
green channel - direct control of RGBW-lighting |
|
blue channel - direct control of RGBW-lighting |
|
white channel - direct control of RGBW-lighting |
|
hue of the HSV-color space, indirect control |
|
saturation of the HSV-color space, indirect control |
|
value, the brightness of the HSV-color space, indirect control |
|
color temperature of white, indirect control |
|
brightness of the xyY-color space, indirect control |
|
lightness of the L*C*h° CIE color space, indirect control |
|
chroma of the L*C*h° CIE color space, indirect control |
|
hue of the L*C*h° CIE color space, indirect control |
The slider for the color temperature is special as it controls the hue als
well as the saturation at the same time, so that a given color temperature of
white will be set. When you also want to control the brightness it is recommended
to use Y for that.
It is possible to configure the color temperature range that is used for the
T slider by stating it separated by a colon. E.g. T:2000-10000 would
create a slider going from 2000 Kelvin to 10000 Kelvin.
Example: RGB slider

ColorChooser, RGB slider
<colorchooser controls="RGB-r;RGB-g;RGB-b">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser RGB slider</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: RGBW slider
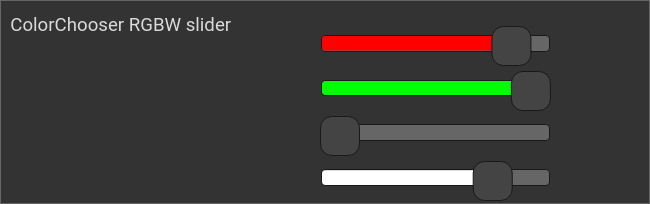
ColorChooser, RGBW slider
<colorchooser controls="RGBW-r;RGBW-g;RGBW-b;RGBW-w">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser RGBW slider</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="RGBW-r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="RGBW-g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="RGBW-b">1/2/61</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="RGBW-w">1/2/62</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: HSV slider
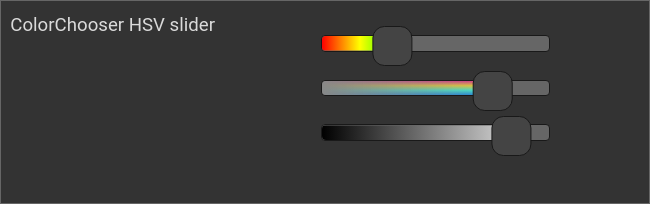
ColorChooser, HSV slider
<colorchooser controls="h;s;v">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser HSV slider</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="h">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="s">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="v">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: color temperature and brightness slider

ColorChooser, color temperature and brightness slider
<colorchooser controls="T:2000-10000;Y">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="3"/>
<label>ColorChooser T and Y slider</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: LCh slider
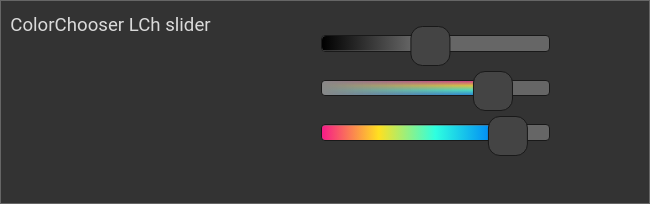
ColorChooser, LCh slider
<colorchooser controls="LCh-L;LCh-C;LCh-h">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser LCh slider</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Widget components: color selection wheel
There are also combined, more complex interactions possible:
|
Color selection wheel with quadratic brightness and saturation selector, HSV color space |
|
Color selection wheel with triangular brightness and saturation selector, HSV color space |
|
Color selection wheel with quadratic brightness and saturation selector, L*C*h° CIE color space |
|
Color selection wheel with triangular brightness and saturation selector, L*C*h° CIE color space |
Example: combined chooser box
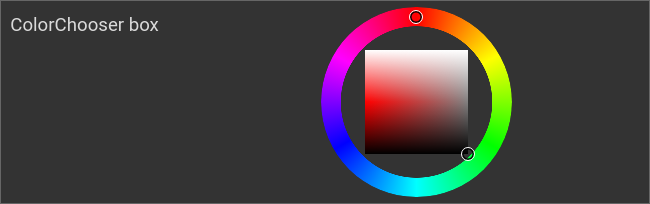
ColorChooser, combined chooser: box
<colorchooser controls="box">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser box</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: combined chooser triangle
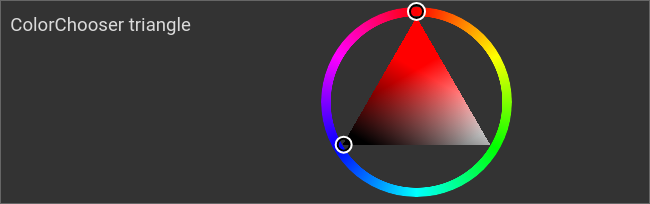
ColorChooser, combined chooser: triangle
<colorchooser controls="triangle">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser triangle</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: combined chooser LCh-box
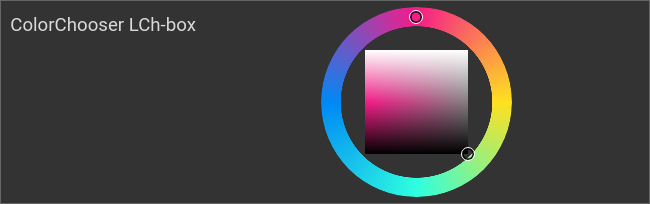
ColorChooser, combined chooser: LCh-box
<colorchooser controls="LCh-box">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser LCh-box</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Example: combined chooser LCh-triangle
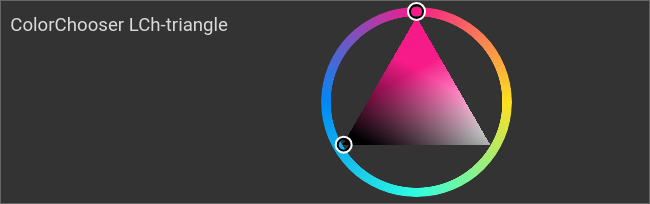
ColorChooser, combined chooser: LCh-triangle
<colorchooser controls="LCh-triangle">
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>ColorChooser LCh-triangle</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Note
In the simple mode it is recommended to use the color selection wheel in the HSV color space. In the professional mode, when the chromaticity coordinates are configured, the L*C*h° color space should be used for best color alignment.
Dim curves
The eye does not measure brightness in a linear fashion but in a logarithmic way to be able to see at a dark night as well as during high noon. Different lighting systems, like DALI, take that into account and thus use a non linear dim curve, so that the brightness of the light has a better match to the selected dim value. Although this is a desirable mechanism it prevents the mixing of different light colors as this requires a linear dim curve.
Using the attributes r_curve, g_curve, b_curve and w_curve it
is possible to configure the dim curve used by the lighting system and
compensate it for color mixing. Apart from defining a look up table (intended
for the use at the professional mode) the keywords linear, exponential
and logarithmic allow a simple use of the most common types of curve.
Note
Configuring a dim curve is only required when the communication is
done in raw color components (r, g, b and perhaps w).
Using a complete color in HSV or - in the best case - as xyY color
a dim curve isn’t necessary.
The correct value is stated in the documentation of the lighting system, but it is important to consider the lights, the drivers and the bus gateways, as each component might use a non linear behavior.
It is possible to do a quick check whether the selected curve is right or way off. For that the red channel has to be set to 100%, the green to 50% and the blue to 0% (when you are also using a white channel is must also be 0%). When the dim curves are set correctly the light color should now be a saturated orange.
When the light color is different and no curve has been configured this table shows the correct curve to use for compensation:
target color |
real color |
dim curve to use for compensation |
—— |
—— |
logarithmic |
—— |
—— |
linear |
—— |
—— |
exponential |
In most cases it is sufficient to select the correct dim curve for a good
consistent color. But when you select a brightness of 100% and a saturation
of 0% and have a color tint and not a neutral white you can use r_strength,
g_strength and b_strength to correct the color.
This is also possible with a RGBW light source but the judgement by eye will
be quite demanding. In this case it’s better suited to use a measurement
device as described in the professional mode.
Professional mode
For professional applications like architecture, art galleries or yachting the simple mode can be easily upgraded to the professional mode where the color chooser can be used for true color selecting.
Note
Best results require a calibrated display. As, on purpose, only the sRGB color space is used for showing the widget also uncalibrated devices (like a smart phone or a tablet computer) should still have acceptable performance in most cases. Although only the sRGB color space is used the ColorChooser does allow the selection of all colors that the lighting system does allow.
The difference between the professional and the simple mode is that the colorimetric locus and the dim behaviour of the channels of the light source are configured.
Best results will be reached by measuring the colorimetric locus of the red,
green, blue and (when available) white channel by using a spectral photometer
and stating the measured x and y coordinates of the CIE xyY color space
as well as the maximal brightness in the config file. This measurement can also provide
a look up table for the dim curve.
Due to aging of the light source those values should be regularly remeasured,
just like any display calibration. The frequency of this measurement depends
on the required color accuracy.
It is still possible to get good results without a measurement device when the
data sheet of the used light source is available. When no values for the x
and y coordinates are given but instead the wave length of the color it
can be used alternatively. Although this would work only for a monochromatic
light source like a laser, the widely used RGB-LEDs can still be assumed to be
nearly monochromatic. For the white channel it is possible to use the
color temperature instead of the xy coordinates. A deviation from the
black body curve can’t be stated, in such a case the x and y
coordinates must be used.
The configured brightness does not need to follow a specific physical unit (like lumen or lumen/meter for LED stripes) as the ColorChooser is using only relative values.
For a best match between the displayed color and that from the light the
widget element should not be used in the HSV but in the L*C*h° mode. The
bus communication should use the xy, xyY or L*a*B* color space as then
the conversation to control the light source is happening close to it
reducing any errors in between. A communication in the HSV color space might
still work. A direct control by RGB or RGBW values would require an accurate
configured dim curve.
Note
The ColorChooser is using internally the CIE xyY color space. For the conversion in the L*a*b* and the L*C*h° color space it is using the D65 light with a 10° standard observer.
Example of a ColorChooser for the OSRAM LINEARlight FLEX Colormix RGBW LED stripe “LF700RGBW-G1-830-06” with the datasheet data and a control via DALI:
<colorchooser
r_wavelength="622" r_strength="80" r_curve="logarithmic"
g_wavelength="534" g_strength="196" g_curve="logarithmic"
b_wavelength="468" b_strength="21" b_curve="logarithmic"
w_x="0.4290" w_y="0.4010" w_strength="400" w_curve="logarithmic"
controls="LCh-triangle">
<layout rowspan="4" colspan="6"/>
<label>LED Strip</label>
<address transform="DPT:242.600" mode="read" variant="xyY">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:242.600" mode="write" variant="xyY">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Warning
It is technically possible to use multiple address elements with different
color space types like RGB and HSV. It is also technically possible
to use RGB-R, RGB-G, RGB-B and at the same time RGB.
Although it might seem to work it can have unwanted side effects leading to the display of a wrong color, so it should be prevented and be considered a misconfiguration.
Note
It is recommended to use a bus communication where all color components are
stated in the same data type (e.g. rgb instead of RGB-r, RGB-g
and RGB-b). Otherwise it is possible that for short time periods
after an external change of the color artefacts in the displayed or
animated color are shown.
Note
When multiple ColorChooser are used for the same light (e.g. in one configuration or by opening the CometVisu in two browsers) it is possible that both will show a slightly different color. This happens when a color is selected that isn’t contained in the color space used on the bus communication. This happens most likely with a ColorChooser in LCh mode and RGB mode for communication.
Changing the communication to xyY mode will solve this issue.
Settings
For a general understanding of how the configuration files are structured and what elements and attributes are it is recommended to read this section first: Basics.
The behaviour and appearance of the Info widget can be influenced by using certain attributes and elements. The following tables show the allowed attributes and elements and their possible values. The screenshots show, how both can be edited in the editor.
Attributes underlined by ….. are mandatory, all the others are optional and be omitted.
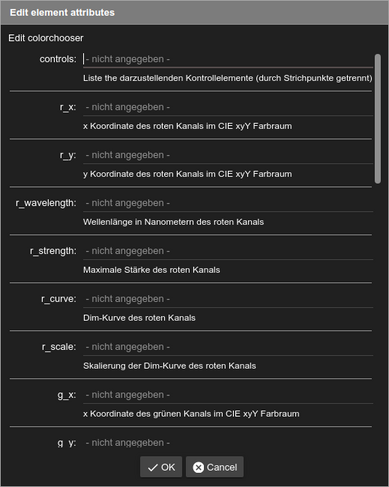
Allowed attributes in the colorchooser-element
Element |
Attribute |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Name |
Content |
Description |
||
colorchooser |
controls |
string |
List of controls to show (separated by semicolons) |
|
r_x |
decimal |
x coordinate of the red channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
r_y |
decimal |
y coordinate of the red channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
r_wavelength |
decimal |
Wavelength in nanometers of the red channel |
||
r_strength |
decimal |
Maximal strength of the red channel |
||
r_curve |
string |
Dim curve of the red channel |
||
r_scale |
decimal |
Scaling of the dim curve of the red channel |
||
g_x |
decimal |
x coordinate of the green channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
g_y |
decimal |
y coordinate of the green channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
g_wavelength |
decimal |
Wavelength in nanometers of the green channel |
||
g_strength |
decimal |
Maximal strength of the green channel |
||
g_curve |
string |
Dim curve of the green channel |
||
g_scale |
decimal |
Scaling of the dim curve of the green channel |
||
b_x |
decimal |
x coordinate of the blue channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
b_y |
decimal |
y coordinate of the blue channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
b_wavelength |
decimal |
Wavelength in nanometers of the blue channel |
||
b_strength |
decimal |
Maximal strength of the blue channel |
||
b_curve |
string |
Dim curve of the blue channel |
||
b_scale |
decimal |
Scaling of the dim curve of the blue channel |
||
w_x |
decimal |
x coordinate of the white channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
w_y |
decimal |
y coordinate of the white channel in the CIE xyY color space |
||
w_strength |
decimal |
Maximal strength of the white channel |
||
w_curve |
string |
Dim curve of the white channel |
||
w_scale |
decimal |
Scaling of the dim curve of the white channel |
||
send_on_finish |
true or false |
Send only when the slider is released. |
||
Allowed child-elements and their attributes
Element |
Attribute |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Structure |
Name |
Content |
Description |
|
|
colspan |
decimal |
Amount of columns this widget should be wide. |
|
colspan-m |
decimal |
Overrules the amount of columns on a medium screen. |
||
colspan-s |
decimal |
Overrules the amount of columns on a small screen. |
||
rowspan |
decimal |
Amount of rows this widget should be high. |
||
x |
string |
Horizontal position of the widget for 2D pages. |
||
x-s |
string |
Horizontal position of the widget for 2D pages on a small screen. |
||
x-m |
string |
Horizontal position of the widget for 2D pages on a medium screen. |
||
y |
string |
Vertical position of the widget for 2D pages. |
||
y-s |
string |
Vertical position of the widget for 2D pages on a small screen. |
||
y-m |
string |
Vertical position of the widget for 2D pages on a medium screen. |
||
z |
string |
Reserved for future use. |
||
width |
string |
Width for the widget for 2D pages. |
||
width-s |
string |
Width for the widget for 2D pages on a small screen. |
||
width-m |
string |
Width for the widget for 2D pages on a medium screen. |
||
scale |
true or false |
Enable/Disable scaling layout values relative to backdrop on 2d pages (default: true). |
||
scale-s |
true or false |
Enable/Disable scaling layout values relative to backdrop on 2d pages on a small screen (default: true). |
||
scale-m |
true or false |
Enable/Disable scaling layout values relative to backdrop on 2d pages on a medium screen (default: true). |
||
Element |
Attribute |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Structure |
Name |
Content |
Description |
|
|
name |
string |
Name of the icon registration. |
|
type |
string |
|||
flavour |
string |
Selection of a display variant. See also Flavour. |
||
color |
string |
Color of the icon in CSS notation (e.g. #1188FF). |
||
styling |
string |
Change the color of the displayed value depending on its value. See also Styling |
||
class |
string |
Add this value to the CSS class so that it can be formatted by a user provided style sheet. |
||
|
string |
Text to display a label for the widget. |
||
Element |
Attribute |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Structure |
Name |
Content |
Description |
|
|
transform |
string |
Transformation of the bus system value to be shown. |
|
mode |
disable, read, write or readwrite |
“disable” deactivates the communication, “read” will only fetch data from the backend, “write” will only write to it and an address with “readwrite” will be both, read from and written to. |
||
variant |
string |
|||
format-pos |
decimal |
Position for format string when multiple addresses are used. |
||
selector |
string |
Only MQTT: JSON selector |
||
qos |
decimal |
Only MQTT: QoS |
||
retain |
true or false |
Only MQTT: retain flag |
||
ignore-error |
true or false |
Only MQTT: ignore decode errors. |
||
|
string |
The GA (like: 12/0/7) for KNX-backends, the item name for openHAB-backend or the MQTT topic |
||
Elements in the editor
Important
When you need to address each color (red, green and blue) individually you
need to add a group address with corresponding variant each. For
OpenHAB Color Items or one of the combined KNX data types this does not hold,
here it is e.g. possible to use a variant="rgb" instead.
Valid values for variant are:
|
Red channel of RGB lighting |
|
Green channel of RGB lighting |
|
Blue channel of RGB lighting |
|
Shortcut for |
|
Shortcut for |
|
Shortcut for |
|
Combined data type of RGB lighting |
|
Red channel of RGBW lighting |
|
Green channel of RGBW lighting |
|
Blue channel of RGBW lighting |
|
White channel of RGBW lighting |
|
Combined data type of RGBW lighting |
|
Hue channel of HSV controlled lighting |
|
Saturation channel of HSV controlled lighting |
|
Value channel of HSV controlled lighting |
|
Combined data type of HSV controlled lighting |
|
x channel of xyY controlled lighting |
|
y channel of xyY controlled lighting |
|
Y channel of xyY controlled lighting |
|
Combined data type of xyY controlled lighting |
|
Combined data type of xyY controlled lighting |
Note
The variant used for communication does not necessarily be similar to
the used widget elements as defined by controls. It is valid to use
a ColorChooser with a HSV control and RGB bus communication.
Examples
It is possible to manually edit the visu_config.xml and add an entry for the Info widget.
Caution
Make sure that you only use UTF-8 encoded characters by settings the encoding in your XML-editor to UTF-8 mode!
<colorchooser>
<layout colspan="6" rowspan="4"/>
<label>RGB kitchen</label>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="r">1/2/59</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="g">1/2/60</address>
<address transform="DPT:5.001" mode="readwrite" variant="b">1/2/61</address>
</colorchooser>
Footnotes