Caution
This is the documentation for the current development branch of the CometVisu. It is possible that some of the described features are not yet available in the current release.
Also there might be lots of errors in this documentation as some parts of the content have been translated by an online translation service.
Developer version on the Wiregate
This page explains how to use the developer version of CometVisu on the WireGate. For other devices, this manual is also suitable in principle - however, as there may be differences to WireGate there, we can not address these differences here. So if another platform should be used, then this text must be read intelligently and adapted in the implementation suitably.
Basically, this is the guide for users. Developer information is available to the GitHub CometVisu Wiki refer to.
Without version control
Important
Here the installation of the developer version is explained! Productive systems should only have a released release <https://github.com/CometVisu/CometVisu/releases>.
If you only want to try the latest developer version (of course only at your own risk!), Then you can install it without a version control system. For the “usual” Branch CometVisu/CometVisu->develop you load the file https://github.com/CometVisu/CometVisu/archive/develop.zip and install them as described under: doc: update-other.
However, to install a correct developer version that can be used to restore changes, the following points apply.
With version control
Preparation
Requirement
The code of the CometVisu can be found on GitHub. Since the WireGate brings the git client not pre-installed, you have to install this first.
Installation with packages
On newer Debian based systems git can easily be installed via the command line (eg remote SSH connection) as root with this command:
apt-get install git-core
Installation without packages
Since the current (as of: 12.04.2015) available Git version for the Wiregate is too old (this is incompatible with GitHub), you have to install Git “by hand”. There are two ways to do this. You can install and compile the current Git version yourself - recommended variant - or you can use the master.zip file.
Install the latest Git version yourself and compile
apt-get install tcl
apt-get install tk
apt-get install python-apt
apt-get install python-software-properties
apt-get install zlib1g-dev
apt-get install build-essential autoconf
apt-get install gettext
cd /usr/local/src
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/software/scm/git/git-2.4.1.tar.gz
tar -xzvf git-2.4.1.tar.gz
cd git-2.4.1
make configure
./configure
make
make install
cd ..
rm -rf git-2.4.1
rm git-2.4.1.tar.gz
If the installation/configuration of ‘python-software-properties’ aborts, then the following command helps:
Caution
There are indications that currently (13.01.2016) the next command can damage the WireGate installation! Please only run when you know what you’re doing!
cp -f /usr/bin/python2.5 /usr/bin/python
dpkg --configure -a
The installation can be checked with the following command:
git --version
Use master.zip file
To do this, take the file from
https://github.com/git/git/archive/master.zip
This zip file contains a readme with the make command that you must execute.
If there are difficulties, you may need the following libraries be reinstalled:
apt-get install libexpat1-dev build-essential libcurl4-openssl-dev libssl-dev gettext
At GitHub
If the version control is installed on your own, you have to create an account on GitHub <https://github.com/> __, if you do not have one yet.
On GitHub go to the CometVisu repository under CometVisu / CometVisu right click on “Fork” to create a fork of this repository.
If you now go to your own GitHub page, then on the right side under
“HTTPS clone URL” a URL that you have to remember (or copied to the
clipboard). This URL is in the form https://github.com/<accountname>/CometVisu.git
Installation
It is recommended to install with Git. As fallback stands however, SVN (or Subversion) remains available.
Git
The own fork of the CometVisu is now installed by a simple command:
cd /var/www
git clone https://github.com/<Accountname>/CometVisu.git CometVisuGit
Under certain circumstances, the retrieval via https does not work, then the fork should be initialized via the following command:
cd /var/www
git clone git://github.com/<Accountname>/CometVisu.git CometVisuGit
The result should now be a text similar to this:
Klone nach 'CometVisuGit'...
remote: Counting objects: 20347, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (5220/5220), done.
remote: Total 20347 (delta 14950), reused 20280 (delta 14905)
Empfange Objekte: 100% (20347/20347), 48.50 MiB | 346.00 KiB/s, Fertig.
Löse Unterschiede auf: 100% (14950/14950), Fertig.
Prüfe Konnektivität... Fertig.
Checke Dateien aus: 100% (1175/1175), Fertig.
If cloning has been successful, this version will be listed as origin. Then you can add the main repository as upstream:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/CometVisu/CometVisu.git
Subversion
If the git clone did not work and an error message like
error: The requested URL returned error: 403
warning: remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout.
appeared, it may be that the installed Git version is too old.
If you do not want to install a newer Git version after Installation without packages, you can now use Subversion (as with the previous repository on SourceForge) as an alternative. While this is not the recommended solution, it’s almost as good as direct access with Git.
More information about working with Subversion on GitHub is in the article 1.
To install the CometVisu with Subversion, go to the GitHub page at its
fork (s.o.) on the right side to “You can clone with HTTPS, SSH, or
Subversion.” and click on the word “Subversion”. Now copy the URL under
the now appearing “Subversion checkout URL”. This should be the form
https://github.com/ <accountname>/CometVisu to have.
At the WireGate command line, execute these commands:
cd /var/www
svn co --depth empty https://github.com/<Accountname>/CometVisu CometVisuGitSVN
Wait for something should appear as confirmation text similar to this:
Checkout, Revision 1342.
Now you can continue in the installation and execute these commands:
cd CometVisuGitSVN/
svn up trunk
If many lines with filenames appear on the screen, the command was successful. This is now completed by
svn up --depth empty branches
cd ..
ln -s CometVisuGitSVN/trunk/src visu_git
Congratulations! Under http://wiregate/visu_git/ should now run the CometVisu!
Next steps
Regardless of whether you have installed Git or SVN, you should follow these steps.
In order to be able to save the Visu Config via the editor, write permissions still have to be set up for the file:
chmod a+rw /var/www/visu_git/config/visu_config.xml
The backup folder also needs write permissions:
chmod a+rw /var/www/visu_git/config/backup
And the preview also:
chmod a+rw
/var/www/visu_git/config/visu_config_previewtemp.xml
Now the Demo-Visu is under http://wiregatexxx/visu_git/ and the
Visu-Editor is under http://wiregateXXX/visu_git/editor/ available.
Important
The CometVisu can be completely removed by simply deleting the directory. Also for a new installation (renewed SVN checkout) if the SVN update should not work anymore, the directory must be deleted. It is recommended to save the contents of the directory /config/. Otherwise your own configs will be deleted!
Usage
When everything has been prepared, the version control system was installed and the CometVisu checked out, then you can go into the use.
It should be noted that there are now several repositories due to the distributed structure of the Git and there are also different branches:
CometVisu/CometVisu -> master- the Main repository and main branch. Here are only the official releases.CometVisu/CometVisu -> develop- the development area in the main repository. Here is the main development. The state of the files in this branch should always be functional.CometVisu/CometVisu -> <weitere>- under GitHub->Branches are all other Branches to find. Here are some features for the development industry prepared.<Accountname>/CometVisu -> ...- The branches under the fork. Mostly there master is used or in the development of patches or features extra created a (further) branch, which is closed again after completion and a pull toCometVisu/CometVisu->develop.the local computer (or WireGate) -> ...- local Branches.
This means that there are essentially three different locations for the files:
CometVisu (upstream) <-> ** (origin) <-> local on the WireGate
To keep these locations in sync, several steps must be taken.
Generic
This chapter will describe the synchronization of
CometVisu (upstream) <-> ** (origin)
Update des GitHub Forks
CometVisu (upstream) -> ** (origin)
To take over the last changes of the development branch
CometVisu/CometVisu->develop into your own fork you need a
Pull. The easiest way to do this is via the GitHub page of
your own fork https://github.com/ <accountname>/CometVisu out.
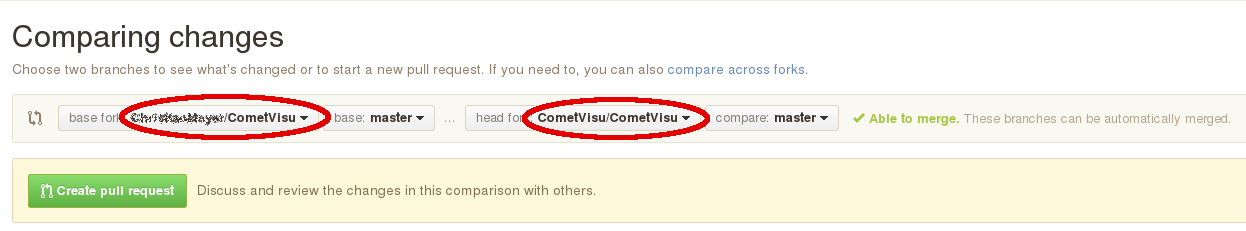
Click on the Pull Request button:

Make sure the base fork matches your own fork
(i.e. <accountname>) and head fork is on CometVisu/CometVisu:
Click on Create pull request and on the following page, (where you can enter a corresponding commit comment if needed) again Create pull request.
On the next page you will see (hopefully …) * This pull request can be merged automatically.* - click here again Merge pull request:

At the end you have to click on Configm merge:

Update of the main repository on GitHub
CometVisu (upstream) <- ** (origin)
This step is necessary to make your own changes in the Main Development Branch.
To get from your own fork to CometVisu/CometVisu->develop,
as a Subversion user it’s best to use the GitHub page.This works
in the same way as point # 2 of the section “Update GitHub Forks”,
except that here base fork CometVisu/CometVisu must be listed
and under head fork the <accountname>/CometVisu.
Git
If the installation was done as above, then all branches under
CometVisu/CometVisu are known as upstream and under
<Accountname/CometVisu as origin.
This can be easily done by the command `` git remote -v`` check:
$ git remote -v
origin https://github.com/<Accountname>/CometVisu.git (fetch)
origin https://github.com/<Accountname>/CometVisu.git> (push)
upstream https://github.com/CometVisu/CometVisu.git (fetch)
upstream https://github.com/CometVisu/CometVisu.git (push)
Update on WireGate
** (origin) -> local on WireGate
Unfortunately, working with Git can not be explained in this short manual. Please look up here in suitable sources!
The essential command for this is:
git pull
Update on GitHub
<Accountname> (origin) <- local on WireGate
Publishing your own changes to GitHub requires several (but simple) steps.
By uploading your own changes, <Accountname>/CometVisu will be
updated first. From there you can now use pull request to transfer
these changes to the main repository CometVisu/CometVisu. In
the pull request you can also choose in which branch should be
integrated there. Of course you can also create this pull request
via the command line with Git - or very comfortably via the
GitHub page.
Unfortunately, working with Git can not be explained in this short manual. Please look up here in suitable sources! However, the most basic command in this context is:
git add .
git commit
git push
Subversion
Update on WireGate
<Accountname> (origin) -> local on WireGate
To update the local files on the WireGate use:
cd /var/www/visu_git
svn update .
Update to GitHub
<Accountname> (origin) <- local on WireGate
Publishing your own changes to GitHub requires several (but simple) steps.
Uploading your own changes will now update <Accountname>/CometVisu first.
From there you can now use pull request to transfer these changes to the
main repository CometVisu/CometVisu. In the pull request you can also
choose in which branch should be integrated there.
By the command
svn ci --username <GitHub Login>
own changes can be transferred to your own fork on GitHub